AtlasIntel Polls Bias: The Hidden Truth Behind Polling Data
Have you ever wondered why polls sometimes feel like they're steering public opinion rather than reflecting it? Well, buckle up because we're diving deep into the world of AtlasIntel polls bias. In this article, we'll uncover the secrets behind polling practices, explore potential biases, and help you become a smarter consumer of data. Think of it as your backstage pass to the world of polling, where not everything is as clear-cut as it seems.
AtlasIntel polls have gained significant attention in recent years, but what exactly makes them tick? Are they as neutral as they claim to be, or is there something more going on behind the scenes? As we delve into this topic, we’ll explore how polling bias can shape public perception, influence decision-making, and sometimes even sway entire elections.
This isn’t just about numbers; it’s about understanding the human element that goes into creating polls. From sampling methods to question phrasing, every detail matters. So, if you’re ready to uncover the truth and learn how to navigate the complex world of polling, let’s get started. But first, here’s a quick roadmap to guide you through this article:
- Mix Tvnow Your Ultimate Guide To Streaming Entertainment
- Aquarius Taurus The Cosmic Connection You Need To Explore Right Now
What is AtlasIntel Polls Bias?
Let’s start with the basics. AtlasIntel polls bias refers to the systematic errors or influences that can skew the results of polling data. It’s not just about getting the numbers wrong; it’s about understanding why those numbers might be misleading. Polls are supposed to be a mirror of public opinion, but when bias creeps in, that reflection can become distorted.
AtlasIntel, like many polling organizations, relies on a variety of methods to gather data. However, these methods aren’t foolproof. Factors like sample selection, question wording, and even the timing of the poll can introduce bias. It’s like trying to take a perfect selfie, but the lighting, angle, or even the filter can change how the picture turns out.
Why Should You Care About Polling Bias?
Here’s the thing: polling bias isn’t just some academic concept. It has real-world implications. Think about how polls influence everything from election campaigns to product marketing. If the data isn’t accurate, the decisions based on that data could lead to serious consequences. So, whether you’re a voter, a business owner, or just someone curious about the world, understanding polling bias is crucial.
- Olivia Thrilby The Rising Star Of Hollywoods New Generation
- Bridgerton Kids The Next Generation Of Love And Scandal In High Society
The History of AtlasIntel Polls
AtlasIntel didn’t just pop up overnight. The organization has a rich history that dates back to its founding in the early 2000s. Initially, AtlasIntel focused on providing data-driven insights to corporate clients. Over time, they expanded their reach to include political polling, social research, and even global trend analysis.
What sets AtlasIntel apart is their commitment to innovation. They were one of the first organizations to adopt advanced statistical models and machine learning algorithms in their polling processes. But with great power comes great responsibility, and that’s where the issue of bias comes into play.
Key Milestones in AtlasIntel’s Journey
- 2003: AtlasIntel launches its first major corporate polling project.
- 2008: Enters the political polling arena during the U.S. presidential election.
- 2015: Expands globally, offering insights into international markets and elections.
- 2020: Implements AI-driven analytics to enhance polling accuracy.
Common Types of Polling Bias
Now that we’ve set the stage, let’s talk about the different types of bias that can affect AtlasIntel polls. There’s no one-size-fits-all answer here; bias can take many forms, and each one has its own unique impact on the results.
Sampling Bias
Sampling bias occurs when the sample used in a poll doesn’t accurately represent the population being studied. For example, if a poll only surveys people from urban areas, it might not reflect the opinions of rural populations. This can lead to skewed results that don’t truly represent the broader public.
Question Bias
Question bias happens when the wording of a poll question influences how respondents answer. For instance, asking “Do you support protecting endangered species?” might yield different results than asking “Do you support government intervention to protect endangered species?” The way a question is framed can subtly nudge respondents toward a particular answer.
Response Bias
Response bias occurs when respondents give answers they think the pollster wants to hear, rather than their true opinions. This can happen when sensitive topics are involved, or when respondents feel pressured to conform to social norms.
How Bias Affects Public Opinion
The impact of polling bias on public opinion can’t be overstated. When people see biased poll results, they might form incorrect perceptions about what others think. This can create a feedback loop where public opinion is shaped by flawed data, which in turn influences further polling.
Consider this: if a poll shows one candidate leading by a large margin, voters might assume the race is already decided. This could lead to lower turnout for the opposing candidate, effectively turning a biased poll into a self-fulfilling prophecy.
Real-World Examples
- In the 2016 U.S. presidential election, many polls underestimated support for Donald Trump, leading to widespread surprise when he won.
- In the UK’s Brexit referendum, polls suggested a narrow victory for Remain, but the actual result favored Leave.
Methods to Reduce Polling Bias
So, what can be done to reduce bias in AtlasIntel polls? Fortunately, there are several strategies that polling organizations can employ to improve the accuracy of their data.
Improving Sampling Techniques
One key method is to ensure that the sample used in a poll is as representative as possible. This might involve stratified sampling, where the population is divided into subgroups based on key characteristics, or oversampling certain groups to account for underrepresentation.
Refining Question Design
Another approach is to carefully craft poll questions to minimize bias. This might involve testing different versions of a question to see how they affect responses, or using neutral language to avoid influencing respondents.
Enhancing Data Analysis
Finally, advanced statistical techniques can be used to adjust for bias in the data. For example, weighting the results to account for underrepresented groups can help ensure that the final numbers more accurately reflect the population.
Real-World Case Studies
To better understand how polling bias plays out in real life, let’s look at a few case studies involving AtlasIntel polls.
Case Study 1: The 2020 U.S. Presidential Election
During the 2020 election, many polls predicted a landslide victory for Joe Biden. While he did win, the margins were much closer than expected in several key states. Analysts later identified issues with sampling and response bias as potential factors.
Case Study 2: Global Climate Change Survey
In a global survey on climate change attitudes, AtlasIntel found that respondents from certain regions were more likely to report concern about environmental issues. However, further analysis revealed that response bias might have played a role, as some respondents may have felt pressured to give socially acceptable answers.
Understanding Sampling Techniques
Sampling is the backbone of polling, and understanding how it works is essential for identifying potential bias. There are several common sampling methods used by organizations like AtlasIntel, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Random Sampling
Random sampling involves selecting participants at random from the population. This method is simple but can be prone to errors if the sample isn’t large enough to be representative.
Stratified Sampling
Stratified sampling divides the population into subgroups based on key characteristics, such as age or location, and then randomly selects participants from each subgroup. This helps ensure that all groups are adequately represented.
The Role of Question Design
As we’ve seen, question design is a critical factor in reducing polling bias. The way a question is worded can have a significant impact on how respondents interpret and answer it. Here are a few tips for crafting effective poll questions:
- Use clear and concise language.
- Avoid leading or loaded questions.
- Provide balanced response options.
- Test questions with a small group before rolling them out widely.
Statistical Analysis in Polls
Once the data is collected, statistical analysis is used to interpret the results. This involves applying mathematical models to identify trends and patterns in the data. Advanced techniques like regression analysis and machine learning can help adjust for bias and improve the accuracy of the results.
Key Statistical Concepts
- Margin of Error: A measure of the potential variability in the results.
- Confidence Level: The probability that the true value falls within the margin of error.
- Weighting: Adjusting the data to account for underrepresented groups.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In conclusion, AtlasIntel polls bias is a complex issue that requires careful consideration and attention. While polls can provide valuable insights into public opinion, they’re not infallible. Understanding the potential sources of bias and how to mitigate them is crucial for anyone who relies on polling data to make informed decisions.
So, the next time you see a poll result, take a moment to think about how it was conducted and whether it might be subject to bias. And remember, the best way to combat bias is to stay informed and ask questions.
Now, it’s your turn! Have you ever noticed bias in a poll? Share your thoughts in the comments below, or check out some of our other articles for more insights into the world of data and polling. Let’s keep the conversation going!
- Flixtorto Your Ultimate Streaming Destination For Movies And Series
- Metallica Net Worth The Untold Story Of Rockrsquos Richest Band
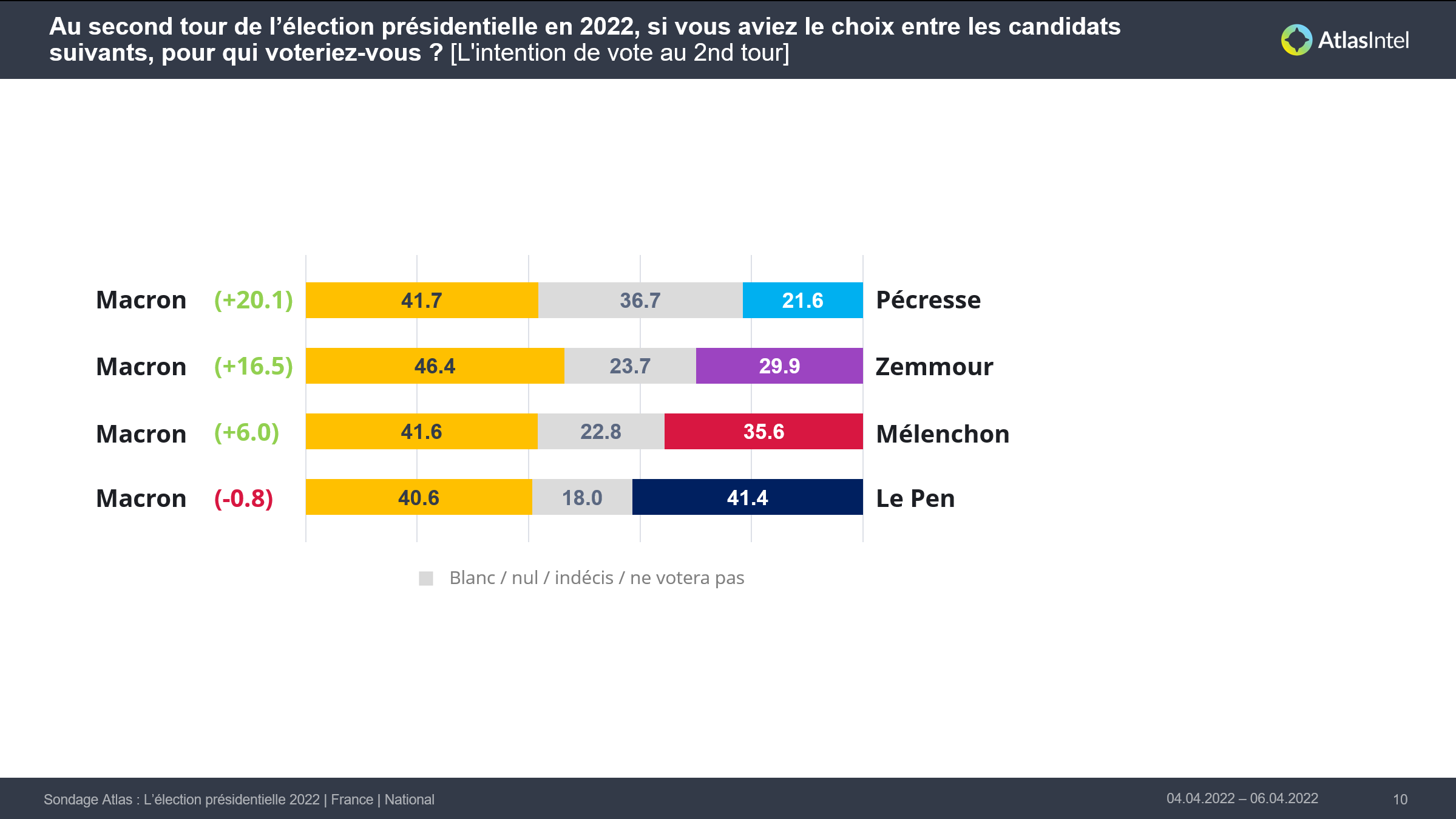
AtlasIntel on Twitter "Atlas Poll France Presidential Election 2nd
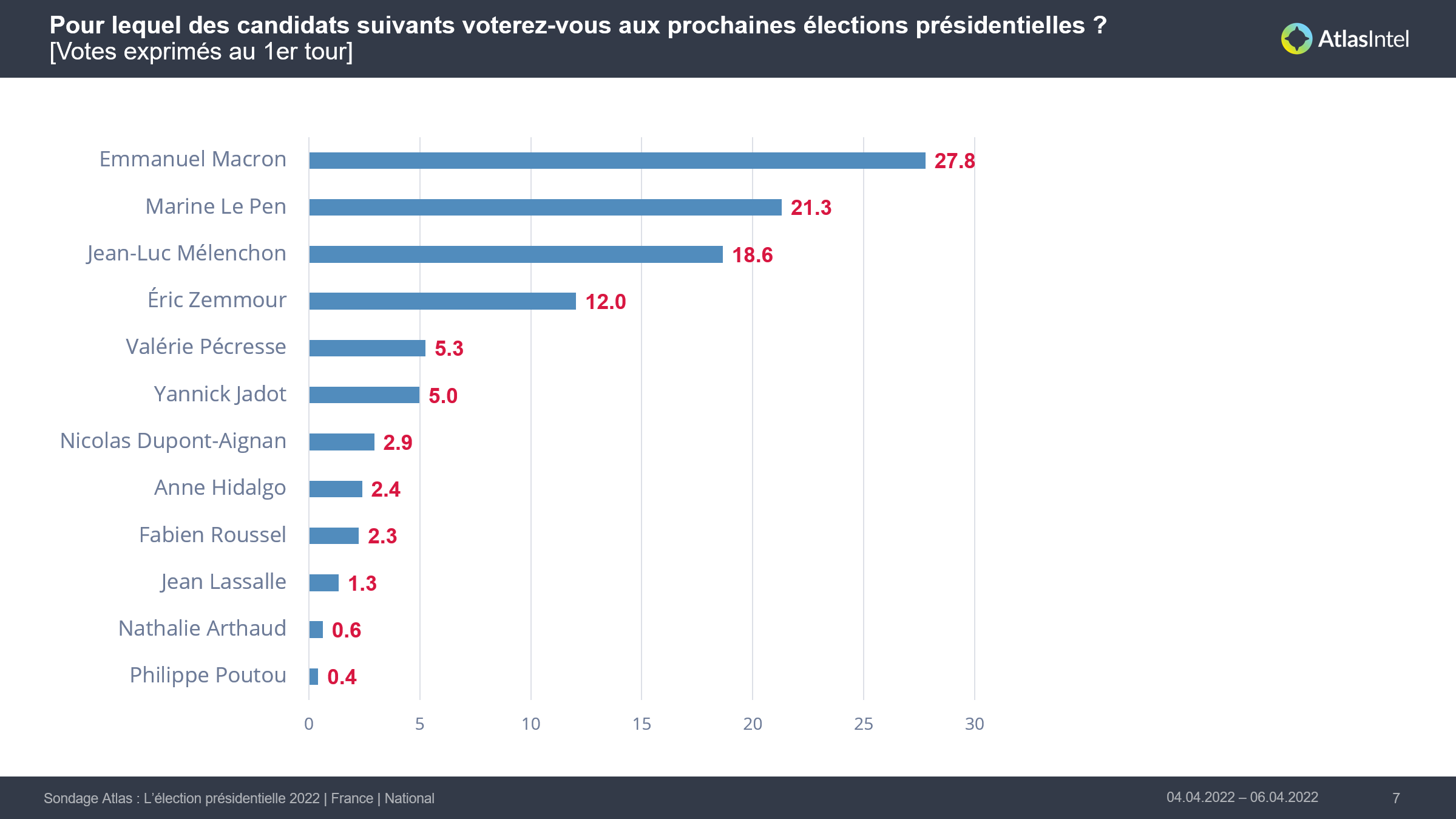
AtlasIntel on Twitter "Atlas Poll France Presidential Election 2nd
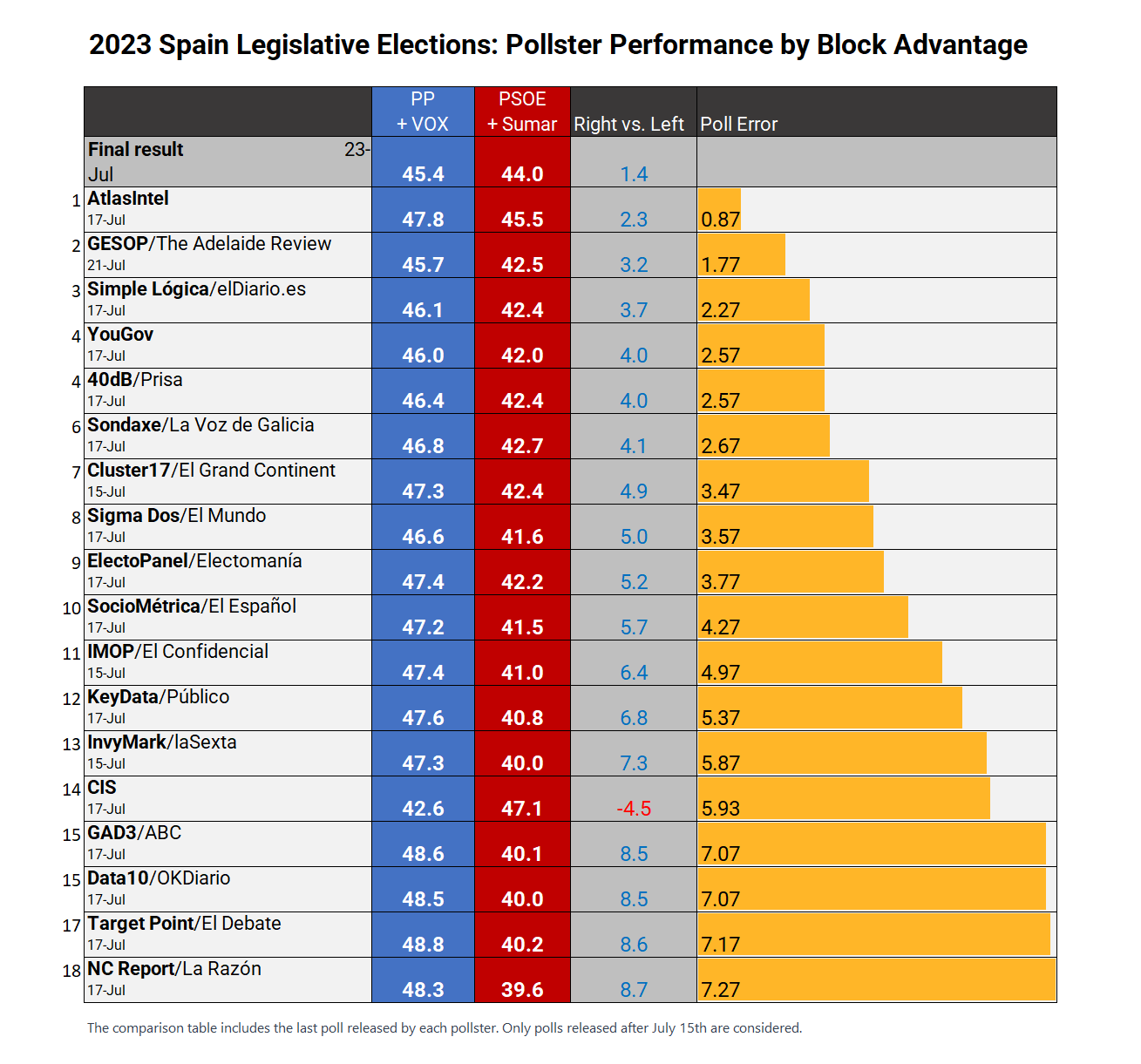
AtlasIntel on Twitter "The Atlas poll was also the most accurate if