What Is The Cubital Region: A Comprehensive Guide
Ever wondered what the cubital region is and why it's so important? This part of your body plays a crucial role in everyday movements, and understanding it can help you take better care of your health. The cubital region, often referred to as the elbow area, is more than just a joint—it's a complex system of bones, muscles, tendons, and nerves working together. Whether you're an athlete, a fitness enthusiast, or simply someone curious about anatomy, this article will give you all the insights you need.
Let's dive right into it. The cubital region isn't just about bending your arm; it's a gateway to understanding how your upper limb functions. From gripping objects to lifting weights, this area is involved in almost every upper body movement. Knowing more about it can help prevent injuries and improve overall mobility. So, buckle up as we explore this fascinating part of the human body.
We’ll cover everything from the anatomy of the cubital region to common injuries, treatment options, and tips for maintaining its health. By the end of this article, you'll have a solid understanding of why this area matters and how to keep it in top shape. Without further ado, let's get started!
- How To Clean Decking Without A Pressure Washer The Ultimate Guide
- Heathrow Airport Code Your Ultimate Guide To Flying Through Londons Hub
Table of Contents
- Anatomy of the Cubital Region
- Key Functions of the Cubital Region
- Common Injuries in the Cubital Region
- Diagnosing Issues in the Cubital Region
- Treatment Options for Cubital Region Problems
- Preventing Cubital Region Injuries
- Effective Exercises for the Cubital Region
- Ergonomics and the Cubital Region
- Busting Myths About the Cubital Region
- Final Thoughts on the Cubital Region
Anatomy of the Cubital Region
The cubital region is essentially the area around your elbow. It's formed by three main bones: the humerus (upper arm bone), the radius, and the ulna (both part of the forearm). These bones come together to form a hinge joint, allowing for flexion and extension movements. But there's more to it than just bones. Surrounding this joint is a network of muscles, tendons, ligaments, and nerves that ensure smooth and controlled motion.
One of the key structures in the cubital region is the ulnar nerve, which runs through the famous "funny bone" area. This nerve is responsible for sensation in parts of your hand and controlling certain muscles. Another important feature is the biceps tendon, which attaches the biceps muscle to the radius bone, enabling you to flex your elbow.
- Anna Burnett The Rising Star Whorsquos Capturing Hearts Around The Globe
- How Many Seats Are In The Wells Fargo Center Your Ultimate Guide To This Iconic Venue
Understanding the anatomy of the cubital region helps explain why injuries here can be so painful and limiting. From tennis elbow to nerve compression, each component plays a role in how well your arm functions. So, let's break it down further in the next section.
Key Structures in the Cubital Region
Here’s a quick rundown of the main structures that make up the cubital region:
- Humerus: The upper arm bone that connects the shoulder to the elbow.
- Radius: One of the two forearm bones, located on the thumb side.
- Ulna: The other forearm bone, located on the pinky side.
- Ulnar Nerve: A major nerve running through the elbow, responsible for sensation and motor control.
- Biceps Tendon: Connects the biceps muscle to the radius bone, allowing elbow flexion.
Key Functions of the Cubital Region
The cubital region isn’t just about bending your arm; it’s a powerhouse of movement. It allows you to perform a wide range of activities, from simple tasks like picking up a cup to complex movements like throwing a ball. The primary functions include flexion (bending the elbow), extension (straightening the arm), and supination/pronation (rotating the forearm).
These movements are made possible by the intricate coordination of muscles and tendons. For instance, the brachialis muscle is primarily responsible for elbow flexion, while the triceps brachii handles extension. Meanwhile, the biceps and supinator muscles work together to rotate your forearm.
Understanding these functions highlights the importance of maintaining the health of the cubital region. Any disruption in this delicate balance can lead to discomfort, pain, or even loss of function.
Everyday Uses of the Cubital Region
Think about your daily routine. Whether you're typing on a keyboard, carrying groceries, or brushing your teeth, the cubital region is hard at work. Here are some examples:
- Typing: Requires constant forearm rotation and wrist support.
- Lifting: Engages the biceps and triceps to bend and straighten the elbow.
- Grooming: Uses fine motor skills controlled by the ulnar nerve.
Common Injuries in the Cubital Region
Despite its strength, the cubital region is prone to injuries due to its frequent use and exposure to stress. Some of the most common issues include tennis elbow, golfer's elbow, and ulnar nerve entrapment. These conditions can arise from repetitive motions, poor ergonomics, or sudden trauma.
Tennis elbow, medically known as lateral epicondylitis, occurs when the tendons on the outside of the elbow become inflamed. On the other hand, golfer's elbow, or medial epicondylitis, affects the tendons on the inside. Both conditions cause pain and weakness, making it difficult to grip objects.
Ulnar nerve entrapment, often called "cubital tunnel syndrome," happens when the nerve gets compressed near the elbow. This can lead to numbness, tingling, and weakness in the hand.
Symptoms of Cubital Region Injuries
Recognizing the symptoms early can help prevent further damage. Look out for:
- Persistent pain in the elbow or forearm.
- Weakness when gripping or lifting objects.
- Numbness or tingling in the fingers, especially the pinky and ring finger.
- Swelling or tenderness around the elbow.
Diagnosing Issues in the Cubital Region
If you suspect an injury in your cubital region, it's important to seek professional help. A healthcare provider will typically start with a physical examination, checking for pain, swelling, and range of motion. They might also order imaging tests like X-rays or MRI scans to get a clearer picture of what's going on.
In some cases, nerve conduction studies may be necessary to assess the health of the ulnar nerve. These tests measure how well the nerve transmits signals, helping to pinpoint the location and severity of any damage.
Early diagnosis is key to effective treatment. Ignoring symptoms can lead to chronic issues that are harder to manage.
Diagnostic Tests for the Cubital Region
Here are some of the tests your doctor might recommend:
- X-rays: To check for fractures or bone abnormalities.
- MRI: For detailed images of soft tissues like muscles and tendons.
- Nerve Conduction Studies: To evaluate nerve function.
Treatment Options for Cubital Region Problems
Once a diagnosis is made, your healthcare provider will recommend a treatment plan tailored to your specific condition. Options range from conservative measures like rest and physical therapy to more invasive procedures like surgery. The goal is always to reduce pain, improve function, and prevent recurrence.
For minor issues, over-the-counter pain relievers and ice packs can provide relief. Physical therapy exercises can strengthen the muscles and improve flexibility. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged tissues or release compressed nerves.
Remember, every case is different, so it's essential to follow your doctor's advice and stick to the prescribed treatment plan.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Before considering surgery, try these non-invasive approaches:
- Rest and avoid activities that strain the elbow.
- Apply ice packs to reduce swelling and pain.
- Take anti-inflammatory medications as directed.
- Engage in physical therapy exercises to strengthen the area.
Preventing Cubital Region Injuries
Prevention is always better than cure. By taking a few simple steps, you can reduce the risk of injuring your cubital region. Start by maintaining good posture and ergonomics, especially if you spend long hours at a desk. Regular stretching and strengthening exercises can also enhance flexibility and resilience.
Using proper techniques during physical activities is another crucial preventive measure. Whether you're lifting weights or playing sports, make sure you're using the correct form to avoid unnecessary strain on your elbow.
Finally, listen to your body. If something feels off, don't ignore it. Early intervention can save you from more serious problems down the line.
Tips for Preventing Cubital Region Injuries
Follow these tips to keep your cubital region healthy:
- Maintain good posture while working or exercising.
- Stretch and strengthen the muscles around the elbow regularly.
- Use ergonomic tools and equipment to reduce strain.
- Avoid repetitive motions that put stress on the elbow.
Effective Exercises for the Cubital Region
Exercise is one of the best ways to maintain the health of your cubital region. Focus on strengthening the muscles, improving flexibility, and enhancing nerve function. Here are some exercises you can try:
Wrist Flexor Stretch: Extend your arm in front of you with your palm facing up. Use your other hand to gently pull back on your fingers until you feel a stretch in your forearm. Hold for 15-30 seconds and repeat.
Bicep Curls: Using light weights, perform slow and controlled curls to strengthen the biceps tendon. Keep your elbows close to your sides for maximum benefit.
Ulnar Nerve Glide: This exercise helps improve nerve mobility. Start with your arm extended and palm facing down. Slowly bend your wrist backward and then forward, gliding the nerve through its pathway.
Sample Workout Plan for the Cubital Region
Create a routine that includes these exercises:
- Wrist Flexor Stretch – 3 sets of 15-30 seconds.
- Bicep Curls – 3 sets of 10-12 reps.
- Ulnar Nerve Glide – 3 sets of 10 reps.
Ergonomics and the Cubital Region
Ergonomics plays a vital role in protecting the cubital region, especially in workplace settings. Poor workstation setup can lead to repetitive strain injuries and nerve compression. By adjusting your environment to fit your body's needs, you can reduce the risk of these issues.
Invest in an ergonomic chair and desk that promote good posture. Position your keyboard and mouse at a comfortable height to avoid bending your wrist too much. Take regular breaks to stretch and move around, giving your cubital region a chance to rest.
Small changes can make a big difference. Don't underestimate the power of ergonomics in maintaining your overall health.
Workplace Tips for the Cubital Region
Implement these ergonomic tips at work:
- Adjust your chair height so your elbows are at a 90-degree angle.
- Use a wrist rest to keep your hands in a neutral position.
- Take short breaks every hour to stretch and relax your muscles.
Busting Myths About the Cubital Region
There are plenty of misconceptions surrounding the cubital region. Let's clear some of them up:
Myth 1: "You can't injure your elbow
- When Was The House Of Burgesses Established Uncovering The Roots Of American Democracy
- How To Get Rare Neko Atsume Cats Your Ultimate Guide To Collecting Them All
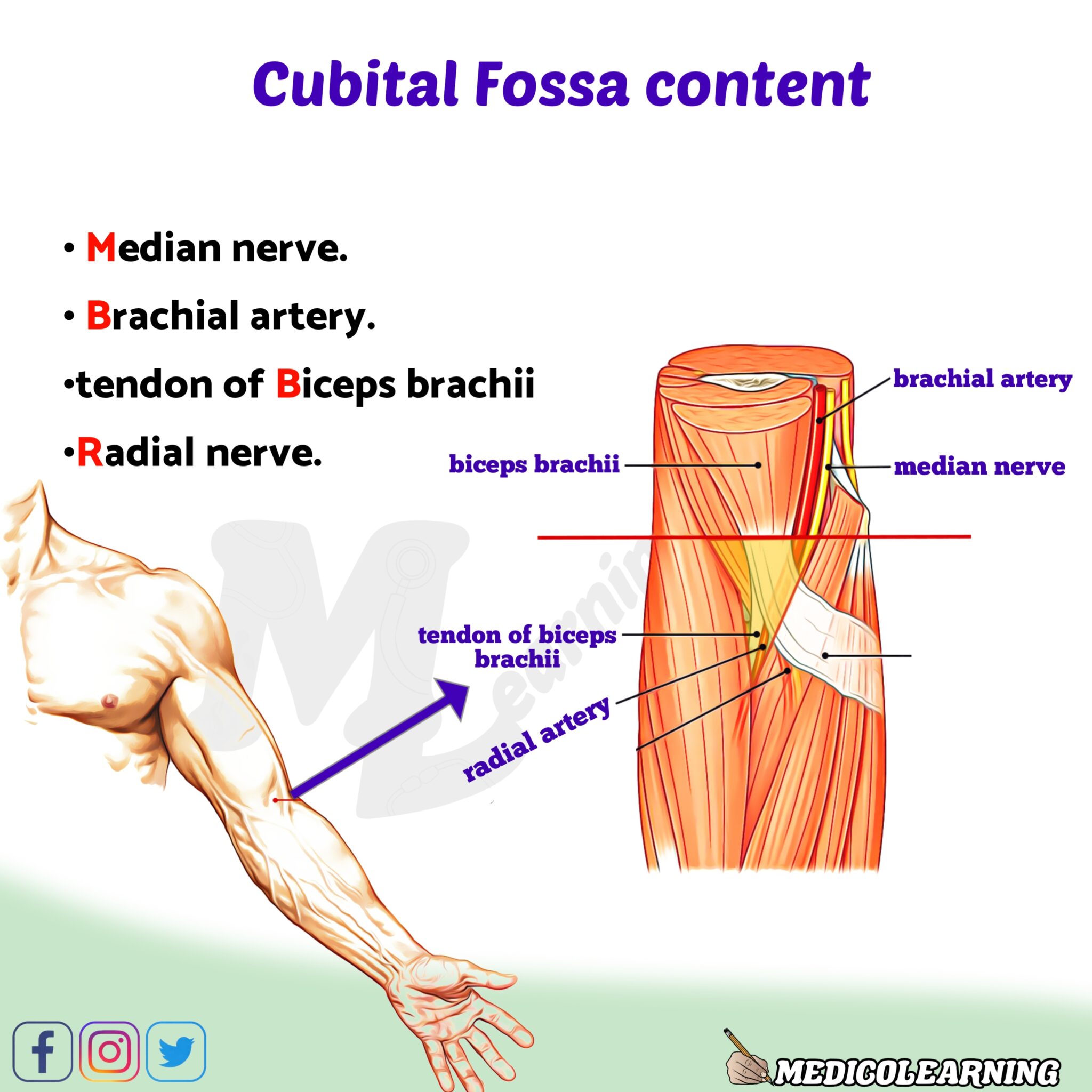
Cubital Fossa Content Mnemonic MedicoLearning

Veias Da Fossa Cubital REVOEDUCA
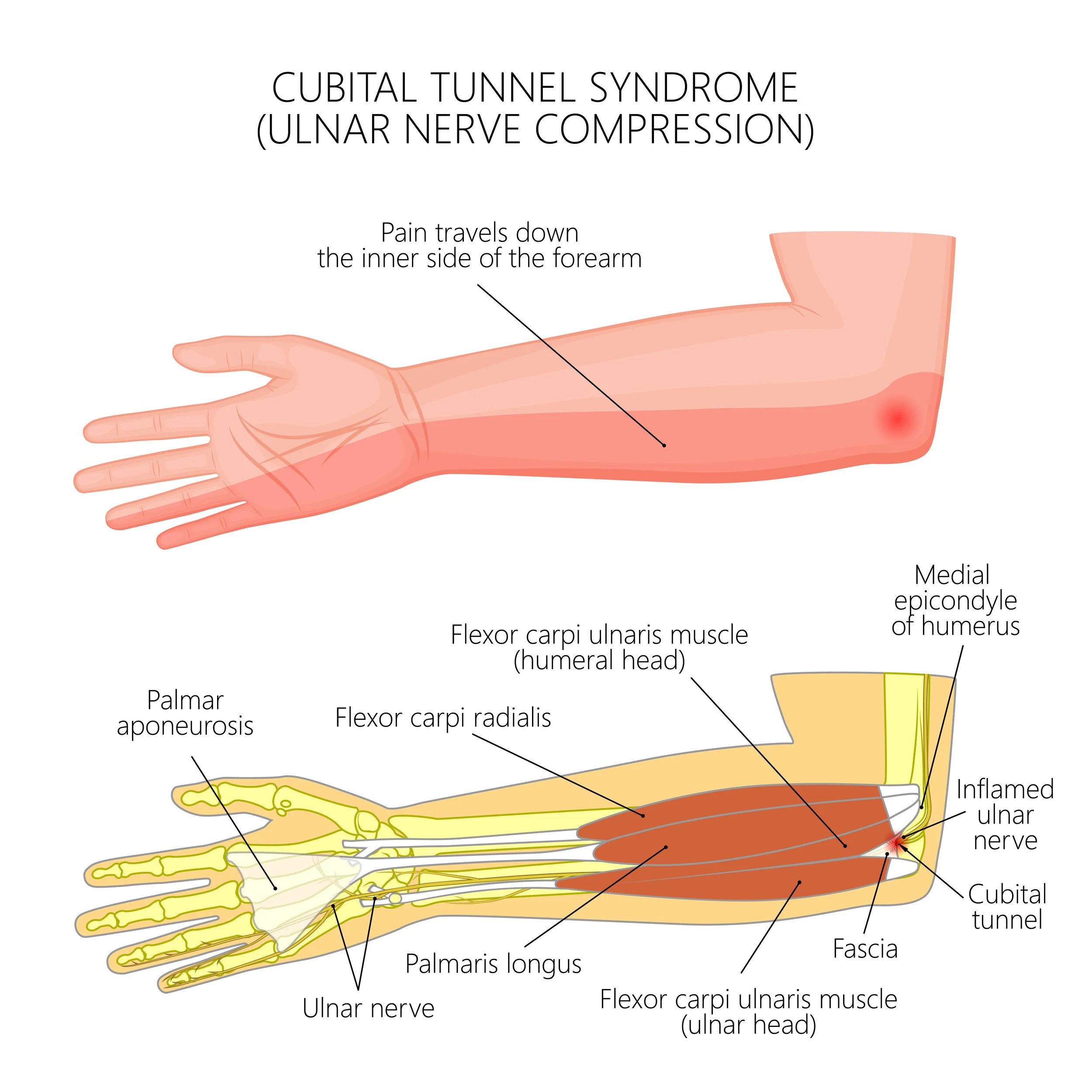
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Raleigh Hand Surgery — Joseph J. Schreiber, MD